 SpringBoot其他功能
SpringBoot其他功能
# YAML文件
YAML: YAML Ain't Markup Language™
- 设计目标,就是方便人类读写
- 层次分明,更适合做配置文件
- 使用.yaml或 .yml作为文件后缀
格式
- 大小写敏感
- 键值对写法 k: v,使用空格分割k,v
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。换行
- 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
# 表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略。
- Value支持的写法
- 对象:键值对的集合,如:映射(map) / 字典(dictionary)
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值,如:数组 / 列表(list)
- 字面量:单个的、不可再分的值,如:字符串、数字、bool、日期
# 属性绑定
将容器中任意组件的属性值和配置文件的配置项的值进行绑定
- 给容器中注册组件(@Component、@Bean)
- 使用 @ConfigurationProperties 声明组件和配置文件的哪些配置项进行绑定
常用语法 Person类
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Data
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthDay;
private Boolean like;
private Child child;
private List<Dog> dogs;
private Map<String, Cat> cats;
}
@Data
class Child {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthDay;
private List<String> text;
}
@Data
class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Data
class Cat {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
配置文件
application.yaml文件
person:
name: 张三
age: 18
birthDay: 2025/10/10 12:12:12
like: true
child:
name: 李四
age: 20
birthDay: 2018/10/10
text: ["abc","def"]
dogs:
- name: 小黑
age: 3
- name: 小白
age: 2
cats:
c1:
name: 小蓝
age: 3
c2: {name: 小绿,age: 2}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 自定义Banner
自定义Banner 类路径添加banner.txt或设置spring.banner.location就可以定制banner
https://www.bootschool.net/ascii
# 自定义 SpringApplication
默认是通过一下来启动项目,还可以通过其他方式来启动项目,创建和启动分开,方便于配置一些启动设置。
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootHelloApplication.class, args);
1
- 通过使用SpringApplication来启动项目
SpringApplication application =new SpringApplication(SpringbootHelloApplication.class)
application.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
//设置监听器
//application.setListeners();
application.run(args);
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
- 通过SpringApplicationBuilder 启动项目
SpringApplicationBuilder builder=new SpringApplicationBuilder().sources(SpringbootHelloApplication.class);
builder.bannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF)
.run(args);
1
2
3
2
3
# Profiles环境隔离
环境隔离能力;快速切换开发、测试、生产环境
步骤:
标识环境:指定哪些组件、配置在哪个环境生效 @Profile 标记组件生效环境
切换环境:这个环境对应的所有组件和配置就应该生效 激活环境:
- 配置文件:spring.profiles.active=prod
- 命令行:java -jar demo.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev 生效的配置 = 默认环境配置 + 激活的环境
# 外部化配置
外部化配置就是可以通过外部的配置文件替代jar内部的配置文件。
假如当前jar所在的目录是/app,外部的配置文件可以有三个位置,
- /app/application.yml 或/app/application-{环境变量}.yml 文件
- /app/config/application.yml 或/app/config/application-{环境变量}.yml 文件
- /app/config/{任意文件夹名称}/application.yml 或/app/config/{任意文件夹名称}/application-{环境变量}.yml 文件
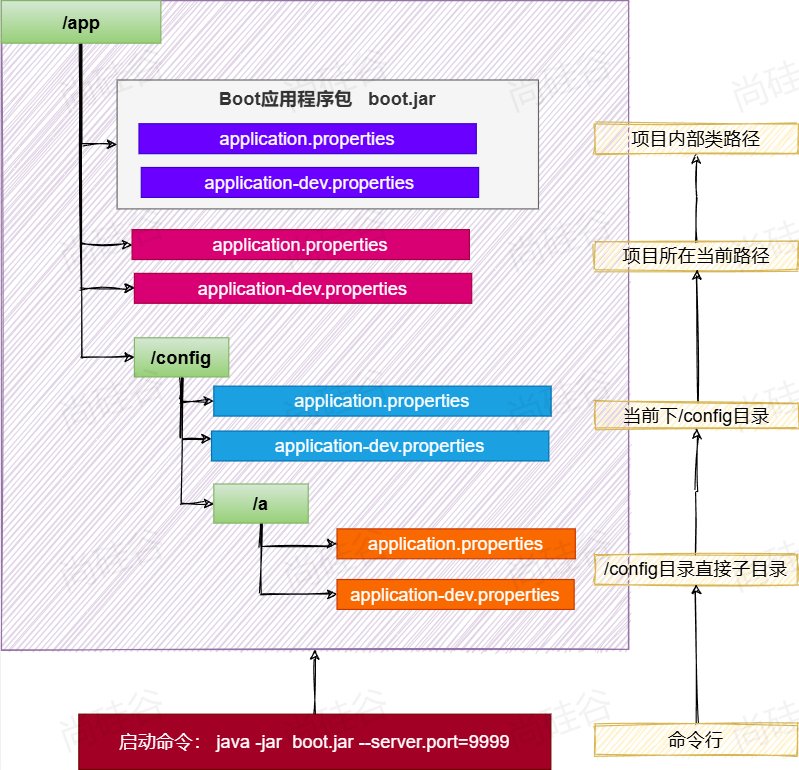
/app代表项目jar当前所在目录
特点:
- 激活优先
- 外部优先
- 激活优先>外部优先
# 断言机制
这是 JUnit 框架提供的测试工具,常用于测试方法的结果是否符合预期。
| 断言方法 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
assertEquals(expected, actual) | 判断两个值是否相等 | assertEquals(5, sum(2,3)) |
assertNotEquals(unexpected, actual) | 判断两个值是否不相等 | assertNotEquals(4, sum(2,3)) |
assertTrue(condition) | 判断条件是否为 true | assertTrue(age > 18) |
assertFalse(condition) | 判断条件是否为 false | assertFalse(list.isEmpty()) |
assertNull(object) | 判断对象是否为 null | assertNull(user.getAddress()) |
assertNotNull(object) | 判断对象是否不为 null | assertNotNull(user.getName()) |
assertSame(expected, actual) | 判断两个对象是否引用同一个对象 | assertSame(obj1, obj2) |
assertNotSame(unexpected, actual) | 判断两个对象是否不是同一个引用 | assertNotSame(obj1, obj3) |
assertArrayEquals(expectedArray, actualArray) | 判断两个数组是否相等(内容相同且顺序一致) | assertArrayEquals(new int[]{1,2}, new int[]{1,2}) |
assertIterableEquals(expected, actual) | 判断两个 Iterable(如 List)是否内容一致 | assertIterableEquals(List.of("a","b"), resultList) |
assertThrows(expectedType, executable) | 判断某个操作是否抛出指定异常 | assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> divide(1,0)) |
assertDoesNotThrow(executable) | 判断某个操作不会抛出异常 | assertDoesNotThrow(() -> doSomething()) |
assertTimeout(Duration, executable) | 判断操作是否在规定时间内完成 | assertTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(1), () -> slowMethod()) |
✅ 总结
- 值比较 → assertEquals / assertNotEquals / assertArrayEquals
- 真假判断 → assertTrue / assertFalse
- 空值判断 → assertNull / assertNotNull
- 引用判断 → assertSame / assertNotSame
- 异常判断 → assertThrows / assertDoesNotThrow
- 性能判断 → assertTimeout
案例
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class AssertionDemoTest {
@Test
void testEqualsAndNotEquals() {
assertEquals(5, 2 + 3, "2+3 应该等于 5");
assertNotEquals(4, 2 + 3, "2+3 不应该等于 4");
}
@Test
void testTrueAndFalse() {
int age = 20;
assertTrue(age > 18, "年龄应该大于 18");
assertFalse(age < 18, "年龄不应该小于 18");
}
@Test
void testNullAndNotNull() {
String str = null;
String name = "SpringBoot";
assertNull(str, "str 应该为 null");
assertNotNull(name, "name 不应该为 null");
}
@Test
void testSameAndNotSame() {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = new String("hello");
assertSame(s1, s2, "s1 和 s2 应该引用同一个对象");
assertNotSame(s1, s3, "s1 和 s3 不应该引用同一个对象");
}
@Test
void testArrayEquals() {
int[] expected = {1, 2, 3};
int[] actual = {1, 2, 3};
assertArrayEquals(expected, actual, "两个数组应该相等");
}
@Test
void testIterableEquals() {
List<String> expected = List.of("a", "b", "c");
List<String> actual = List.of("a", "b", "c");
assertIterableEquals(expected, actual, "两个列表内容应该相同");
}
@Test
void testThrowsAndDoesNotThrow() {
// 判断抛出异常
assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class, () -> {
int result = 1 / 0;
}, "应该抛出 ArithmeticException");
// 判断不会抛出异常
assertDoesNotThrow(() -> {
int result = 1 / 1;
}, "不应该抛出异常");
}
@Test
void testTimeout() {
assertTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(1), () -> {
Thread.sleep(500); // 模拟耗时
}, "方法应该在 1 秒内执行完");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
Last Updated: 2025/11/21, 16:34:23
